Scattered Spider has leveled up in 2025, transforming from teenage SIM-swappers to sophisticated ransomware operators hitting major UK and US organizations. They exploit your own IT support and administrative tools, turning the human element into the primary threat vector.
Meet Scattered Spider
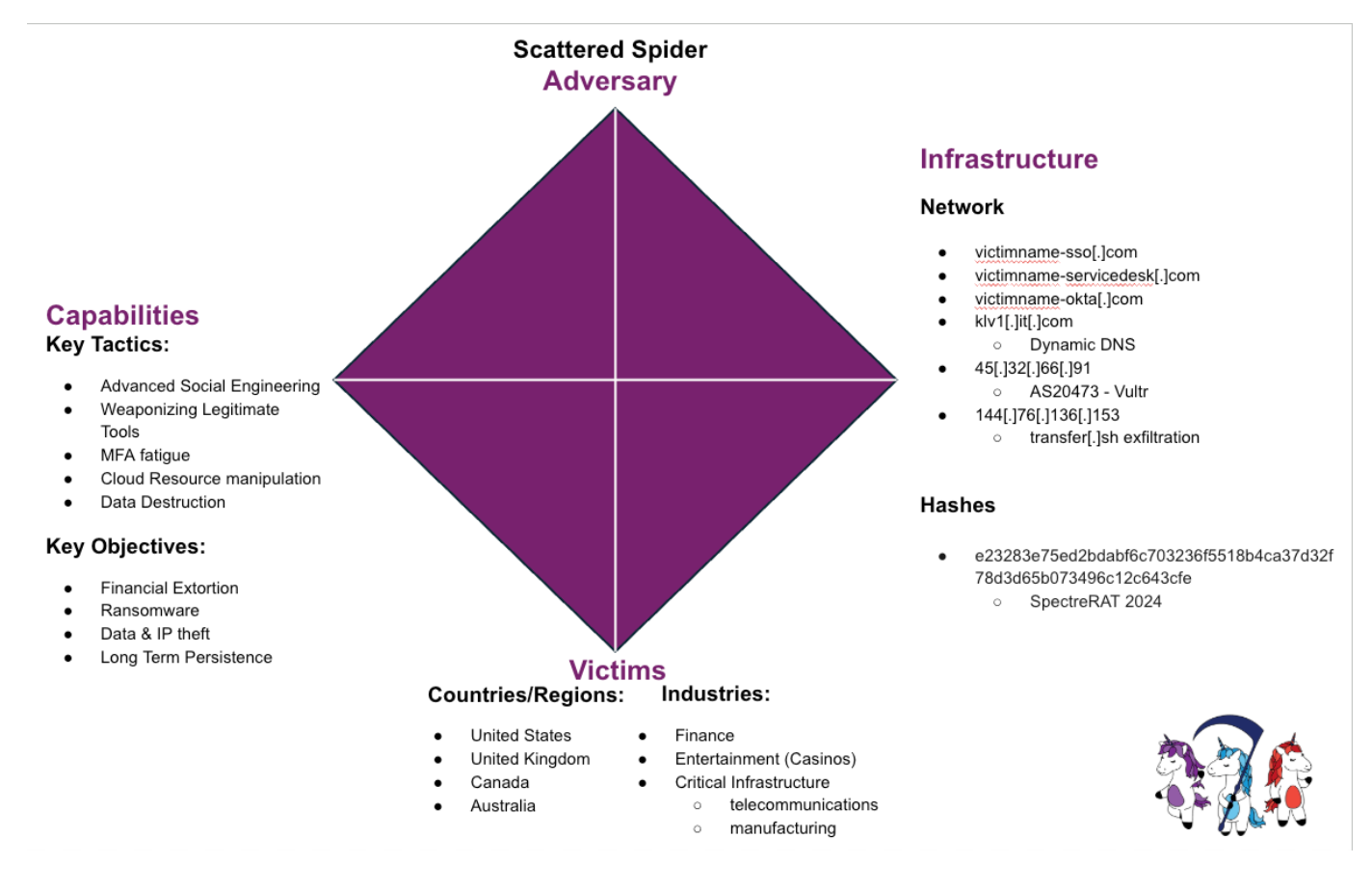
Scattered Spider (also known as UNC3944 or Octo Tempest) emerged from underground communities like The Com, evolving from basic phone scammers into one of 2025’s most dangerous threat actors. Native English speakers aged 19–22 from the US, UK, and Canada, they resemble a cybercrime startup: young, innovative, and exceptionally adaptive.
Notable victims include UK retail giants like Marks & Spencer, Co-op, Harrods, and several airlines. US organizations in hospitality and finance, such as MGM Resorts International, Caesars Entertainment, Visa, PNC, New York Life, and Synchron, make the list as well.
How They Operate
Scattered Spider is a master of social engineering, exploiting both human trust and legitimate administrative tools. Their operations follow a sophisticated playbook:
- Initial Contact – Vishing and Social Engineering
They impersonate employees (“Sarah from accounting”) to manipulate IT support into resetting MFA devices or adding their phone numbers. They know just enough about your organization to sound credible.
- Credential Harvesting
They steal Active Directory databases, browser credentials, and system memory data, targeting privileged accounts like domain administrators to gain unrestricted access.
- Persistence via Legitimate Tools
Scattered Spider deploys multiple legitimate remote management tools (AnyDesk, TeamViewer, ScreenConnect) to maintain multiple access points—even if one is discovered.
- Lateral Movement & Domain Compromise
Using tools such as PSExec and DCSync, they move across networks undetected, escalating privileges while performing system reconnaissance.
- Data Exfiltration & Ransomware Deployment
They exfiltrate sensitive organizational data before deploying ransomware, enabling double extortion: encrypting files while threatening to leak data.
2025 Evolution: From SIM-Swappers to Ransomware Ninjas
Originally leveraging SIM-swapping, MFA fatigue attacks, and SMS/Telegram phishing, Scattered Spider has expanded into fully coordinated post-compromise operations. They even join incident response calls to observe detection efforts, demonstrating deep knowledge of cloud infrastructure and enterprise systems.
Their attacks follow a "wave attack" pattern, obsessively targeting one industry for months before moving to the next.
Detection Considerations
Defenders can enhance detection and response by monitoring for:
- Execution of remote management tools from unusual locations
- Memory dumping attempts targeting LSASS
- Scheduled tasks mimicking system processes
- Bulk file encryption or suspicious compression
- Active Directory enumeration and credential extraction
- Lateral movement via legitimate administration tools
- Sequenced reconnaissance targeting users and systems
Quick Defense Tips
- Harden Your Help Desk – Require manager approval before resetting MFA or adding phone numbers.
- Audit Remote Tools – Maintain an accurate inventory of remote management software.
- Monitor Privileged Accounts – Watch for unusual access and login patterns.
- Train for Vishing – Teach employees how realistic social engineering attacks can appear.
- Deploy Endpoint Detection – Ensure visibility into reconnaissance and post-compromise activity.
Bottom Line
Scattered Spider demonstrates that the most dangerous adversaries aren’t always those with zero-day exploits—they are the ones who can turn your own employees and trusted tools into attack vectors. Organizations must combine behavioral monitoring, strict administrative controls, and robust training to defend against these evolving threats.
References
